The Vikings were one of the most famous seafaring cultures in history renowned for their skill in battle, naval adventures and raids across Europe and beyond between the 8th to 11th centuries. Centuries later, their influence still lives on through fascinating aspects of culture, mythology and not least, physical appearance. Certain facial features have become closely associated with the Nordic region and Viking ancestry that provide insights into the complex interplay between ancient genetics and environmental adaptation over time.
One cannot speak of Vikings without acknowledging the Nordic homeland – Scandinavia. Encompassing Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland and Iceland, this vast northern region shaped both the Viking spirit of exploration as well as distinct Scandinavian facial traits still seen today. The harsh climate presented tremendous challenges for survival that reverberate in our genes. Through this lens we can gain new perspective on the genetic legacy of the Vikings and what it means to have a “Nordic” appearance.
>>> The Mystery of the Viking Dreadlocks
Light Pigmentation and Adaptation
One of the most recognizable Nordic features is fair skin combined with blonde or light brown hair and blue, green or grey eyes. This light pigmentation likely evolved as an important environmental adaptation for absorption of scarce vitamin D from the low sunlight levels in northern latitudes. Those with very fair complexions could sustain sufficient vitamin D production for health even during long, dark winters when direct sun exposure was minimal. The selective pressure of this climate led to light pigmentation predominating in Scandinavian genetic ancestry.
More: Sigurd and Siegfried: A Comparison of the Dragon Slaying Heroes
Strong Bone Structure and High Cheekbones
Beyond pigmentation, Vikings and modern Nordic populations share additional traits reflective of their ancestral homeland’s harsh conditions. Robust bone structure with high cheekbones and prominent brows provide insulation from bitter winds while protecting delicate facial areas. These features allow bodies to conserve precious heat in Scandinavia’s frigid environment. Similarly, broad foreheads may have distributed body heat more efficiently. Such adaptive traits became genetically enriched within Viking descendents.
Deep-Set Eyes and Upturned Eyelids
Perhaps the most recognizable Nordic facial feature is the so-called “Scandinavian eye” shape with deep-set, almond-shaped eyes and slightly upturned outer eyelids. This configuration likely developed for practical purposes – deep eyelid folds shield eyes from blowing snow or sand while the upturned shape enhances peripheral vision useful for spotting dangers on open landscapes and seas. Even today, these distinctive eyes remain a hallmark of Scandinavian heritage.
While less pronounced with admixture over centuries, remnants of ancient Viking ancestry persist through subtle genetic signatures like facial structure. Tracing these ancestral links illuminates past survival strategies that shaped Nordic facial traits valuable for enduring harsh northern environments. The Vikings’ genetic legacy lives on in both the culture and appearance of modern Scandinavians – a fascinating blend of history, genetics and environmental adaptations across a remarkable seafaring people.
More: The Popularity of Mystical and Magical Patterns in Fashion Design
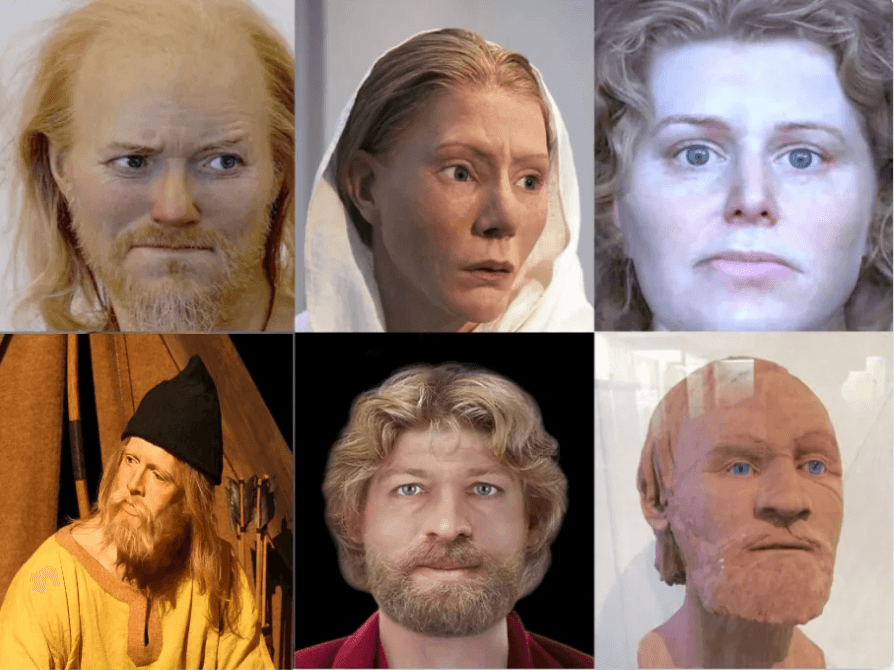

What are common Scandinavian facial features?
Common Scandinavian Facial Features
-
Light Pigmentation
-
Hair and Eyes: Blonde or light brown hair predominates (60–85% of the population), with blue, green, or grey eyes (50–75%). This evolved to maximise vitamin D synthesis in low-sunlight regions.
-
Skin: Fair skin is typical, though modern diversity includes darker tones due to immigration.
-
-
Bone Structure and Eye Shape
-
High Cheekbones and Strong Jawlines: These robust features are common, potentially offering insulation against cold climates.
-
Deep-Set, Almond-Shaped Eyes (“Scandinavian Eyes”): Characterised by upturned outer corners and a protective hood; an adaptation against wind/snow.
-
Broad Foreheads: Especially noted in women, historically linked to Viking ideals of beauty and health.
-
-
Nose and Brow Ridges
-
Straight Noses: A straight, defined nasal bridge is frequent.
-
Prominent Brow Ridges: More pronounced in historical Vikings but still observed in modern Scandinavians.
-
What are the physical features of Scandinavia?
General Physical Features of Scandinavians
Tall Stature
Scandinavian countries rank among the world’s tallest populations:
- Men: 180–182 cm (e.g., Denmark: 182 cm, Sweden/Norway: 180 cm).
- Women: 166–169 cm.
Attributed to genetics, nutrition, and healthcare.
Athletic Build
Lean, muscular physiques are common, linked to active lifestyles (e.g., outdoor activities, sports).
Genetic Diversity
While light features dominate, Scandinavian genetics show influences from:
- Pre-Viking migrations (e.g., Siberian hunter-gatherers, Anatolian farmers) .
- Viking-era mixing with British, Irish, Baltic, and Southern European populations.
Modern diversity is increasing via immigration .
What do Scandinavians typically look like?
Viking facial features (8th–11th centuries) were similar but more gender-neutral and robust than today’s Scandinavians:
| Trait | Viking Era | Modern Scandinavians |
|---|---|---|
| Facial Structure | More prominent brow ridges, stronger jaws; women had masculine traits (e.g., defined jaws). | Softer features; less pronounced gender differences. |
| Hair Colour | Predominantly red (Denmark) or blonde (Sweden); darker hair in 40% due to genetic mixing. | Light hair still dominant (60–85%), but darker shades increasing. |
| Eyes | Mostly light (blue/green); deep-set for climate adaptation. | 50–75% light eyes; “Scandinavian eye shape” remains common. |
| Hygiene/Grooming | Well-kept hair/beards; bleached hair with lye soap; symbolic styles (e.g., “Valkyrie knots”). | High grooming standards persist . |
What are the characteristics of a Viking face?
- “Pure” Viking Genes: Genetic studies show Vikings were diverse (e.g., 40% had non-Scandinavian ancestry). “Viking” was a cultural role, not an ethnicity.
- Universal Blondness: Modern Scandinavians have higher rates of light hair than Vikings, who often had darker hues.
- Facial Stereotypes: Not all Scandinavians fit the “tall, blonde” ideal; Sami populations (indigenous Nordic) exhibit epicanthic eye folds and darker features.
Genetic Legacy Today
Viking DNA: ~10% of Swedes and 6% of Brits carry Viking-related genes.
Physical Signs of Viking Ancestry:
- Robust jawline, high cheekbones, deep-set eyes.
- Red/light hair, tall stature.
- Note: These are not definitive proof due to genetic overlap across Europe.
Defining the Enigmatic Vikings
Table of ContentsLight Pigmentation and AdaptationStrong Bone Structure and High CheekbonesDeep-Set Eyes and Upturned EyelidsWhat
Oct
A Brief History of the Vikings: Who They Were and Where They Came From
Table of ContentsLight Pigmentation and AdaptationStrong Bone Structure and High CheekbonesDeep-Set Eyes and Upturned EyelidsWhat
11 Comments
May
The Dragon Ships of the Vikings: A Deeper Meaning Behind the Iconic Symbol
Table of ContentsLight Pigmentation and AdaptationStrong Bone Structure and High CheekbonesDeep-Set Eyes and Upturned EyelidsWhat
Mar